Project Progress II
Trial for Numerical computation of Permeability—Lattice Boltzmann Method
Background
- Lattice Boltzmann method is a relatively new simulation technique for complex fluid systems. The discrete Boltzmann equation is solved to simulate the flow of a Newtonian fluid with collision models.
- Permeability (Hydraulic Conductivity) is the property of interest.
- If we can come up with the numerical results for permeability, we can do two parts of work: (1) correlate 2-point statistics to permeability through PCA and regression analyses (2) correlate structure properties to permeability (propose new equation).
Progess
Generated randomly packed mono-sized structures (Gravitational Sphere Packing Simulation)
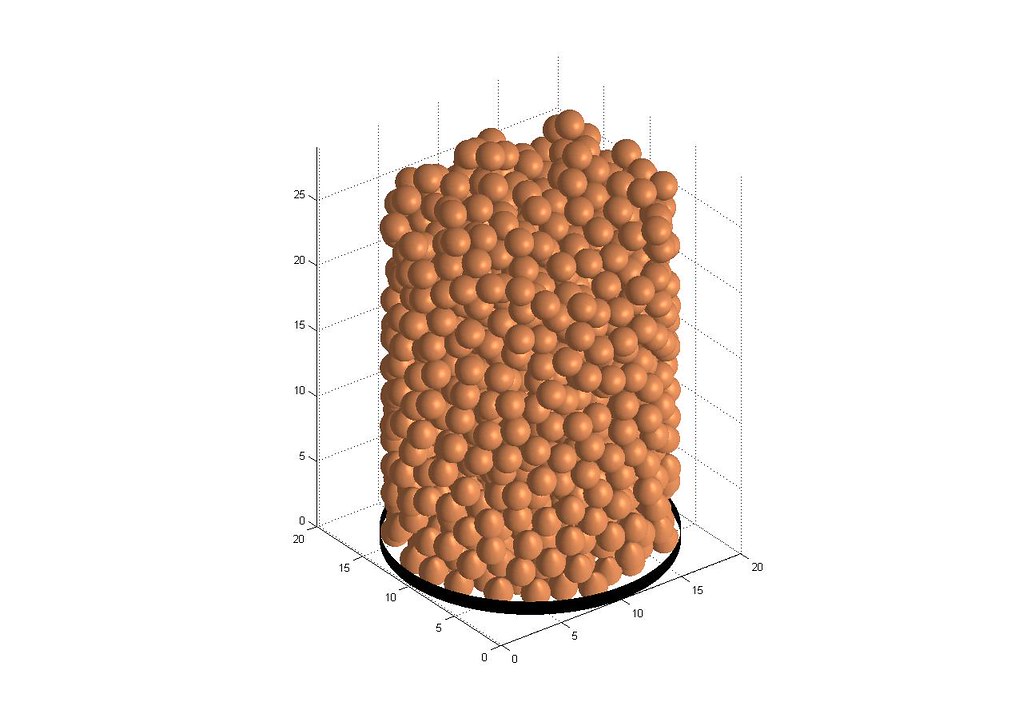
Mono-sized Loosely Packed Particles
3-D LBM simulation of flow through one selected volume

A Sample Sub-volume
Quantified velocity and flow rate

Velocity in X-Z plane (Z is the flow direction)
Next Steps
- Sample 200 volumes from the microstructure to perform LBM simulation
- Convert the lattice units to physical units to obtain permeability for each volume
- 2-point spatial statistics
References
- Lattice Boltzmann Matlab Scripts. http://exolete.com/lbm/
- Wong, R. C. (2003). Strain-induced anisotropy in fabric and hydraulic parameters of oil sand in triaxial compression. Canadian geotechnical journal, 40(3), 489-500.
- Roozbahani, M. M., Graham‐Brady, L., & Frost, J. D. (2014). Mechanical trapping of fine particles in a medium of mono‐sized randomly packed spheres. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics.
- Çeçen, A., Fast, T., Kumbur, E. C., & Kalidindi, S. R. (2014). A data-driven approach to establishing microstructure–property relationships in porous transport layers of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Journal of Power Sources, 245, 144-153.